More than 200 million pounds of post-consumer nylon 6 carpet waste will be kept out of U.S.
landfills each year because of the efforts of environmentally conscious Evergreen Nylon Recycling
LLC (ENR), Augusta, Ga.Honeywell International (formerly AlliedSignal Inc. Performance Polymers),
Colonial Heights, Va., and DSM Chemicals North America Inc. (DCNA), Augusta, Ga., are the joint
venture partners of ENR. The recycling plant, which celebrated its grand opening in November 1999,
is the first economical, large-scale recycling operation for the recovery of first-quality
caprolactam from waste carpet and nylon scrap, according to Richard Lawson, manager, total quality
and training, DCNA. The operation allows nylon to be recycled repeatedly in a truly closed loop.The
recycled nylon can be used in any nylon application, including new carpet, because the process
produces material that is exactly the same as that made from new raw materials. Even the by-product
fibers from the carpet backing will be reclaimed and marketed for use in cement and other products.
Lawson noted the $85 million facility would keep more than 200 million pounds of post-consumer
nylon 6 carpet waste out of U.S. landfills each year. “Carpet represents about 2 percent of total
waste in U.S. landfills, and this business enterprise will reclaim nearly 20 percent of all
discarded nylon 6 carpet,” he said.The demand for recycled content in products continues to rise in
response to environmental, legislative and consumer pressure. A number of vehicle manufacturers are
now reacting by specifying percentages of recycled content in their components. Dave Mezzanotte,
general manager, ENR, and vice president and general manager, Honeywell, said, “This venture allows
us to do something that has never been done before we can make a nylon product live forever. Not
only do our products offer significant environmental benefits, but they are made with the same
quality as virgin nylon products, so you would never know they were recycled.”Lawson added,
“Quality is very important to all products, including nylon. In 1992, DCNA achieved ISO 9001
certification. Through its well- developed quality system, and the extensive in-depth training
given employees, ENRs product quality is second to none.” Nylon 6 Polymer FacilityLawson
explained that, through a polymerization process, the plant converts monomer (caprolactam) to nylon
6 polymer. The monomer feedstock is both virgin monomer from the DCNA plant and recycled monomer
from the ENR plant.The facility consists of two parallel polymer trains and shared utilities. One
polymer line is currently the largest of its kind, producing polymer for carpet fiber applications.
Most of the output of this line is dedicated to one of the largest carpet manufacturers in the
world. The second, smaller line produces polymer for engineering plastic applications, with most of
its output dedicated to DSM Engineering Plastics, a DCNA affiliate company.”This facility is
state-of-the-art with smart instrumentation, computer-based DCS [digital control system] control,
and virtually 100-percent conversion of monomer to polymer,” Lawson said. “Final product is shipped
bulk truck, bulk rail and Gaylord packages.” Carpet CollectionSeveral years ago AlliedSignal
and DCNA launched a pilot facility to recycle carpet. By the end of 1997, the experiment in carpet
recycling was considered a success. The next step was to commercialize the experiment and develop a
facility that could recycle more than 1 billion pounds of post-consumer carpet per year.”In
preparation for this unprecedented commercialization, we have been promoting that industry should
collect carpet,” Lawson said. “This industry of recycling is still in its infancy, but we have
learned a great deal about carpet collection over the past several years and are optimistic that it
will continue to blossom.” Carpet collection is already underway in 75 metropolitan areas
throughout the U.S. In fact, ENR has already collected 70 million pounds of carpet for production.
Carpet retailers can save tens of thousands of dollars each year in landfill fees and other
disposal costs by being part of the collection network, Lawson said.By integrating information and
resources, innovative methods often emerge, as was the case with this joint venture. DCNA In
BriefDCNA is a business unit of the Netherlands-based DSM Fiber Intermediates Business Group. This
integrated international group of companies is active worldwide in chemicals, biotechnological
products and plastic materials. The group has annual sales exceeding $7 billion and employs about
23,000 people at more than 200 sites in Europe, North and South America, Asia, Africa and
Australia.DCNA, originally a joint venture between DSM BV and Pittsburgh-based PPG Industries, was
founded in 1962. Their first venture was a nitrogen fertilizer complex. In 1964, Nipro, Inc. (the
predecessor of DCNA) was organized to manufacture caprolactam, the monomer of nylon 6 used in nylon
fiber production. Subsequent expan-sions of DCNA in 1972 and 1976 made it the largest independent
market supplier of caprolactam in the United States. DSM bought out PPGs interest in the venture in
1973. Construction on the ENR plant in Augusta began in the fall of 1998. Honeywell
(AlliedSignal) In BriefPerformance Polymers is a strategic business unit of Honeywell
Inter-national. Honeywell merged in 1999 with AlliedSignal Inc., an advanced technology and
manufacturing company serving customers worldwide with aerospace products and services, automotive
products, chemicals, fibers, plastics and advanced materials. AlliedSignal was one of the 30 stocks
that make up the Dow Jones Industrial Average and is also a component of the StandardandPoors 500
index. The company employs 70,400 people in some 40 countries.The merged company retained the
Honeywell name and trades under the ticker symbol HON on the New York Stock Exchange. Honeywell is
now part of the Dow Jones Industrial Average, taking the place of AlliedSignal. This merger has
created one of the nations largest companies. In 1999, Honeywell was listed as a Fortune 50
company, with sales of about $24 billion. Honeywell operates in 96 countries and has more than
120,000 employees. The combined market capitalization of Honeywell International exceeds $45
billion. Lawson said the primary reason for the merger was to take advantage of synergies in the
aerospace business.Both Honeywell and AlliedSignal manufactured components used in commercial
aircraft. Their merger is expected to save as much as $750 million by 2002. Some of this savings
will be realized through elimination of redundant jobs, but a large part is expected to come from
an acceleration of AlliedSignals 6 Sigma quality program. The new Honeywell Inter-national will
have businesses in aerospace, control technology, auto-motive, power generation, specialty
chemicals, fibers, plastics, electronics, and advanced materials.ENR is part of Honeywells fibers
and plastics business that makes nylon 6 resin for use in fiber products such as carpet and
industrial textiles, as well as engineering resins that are typically used in automotive
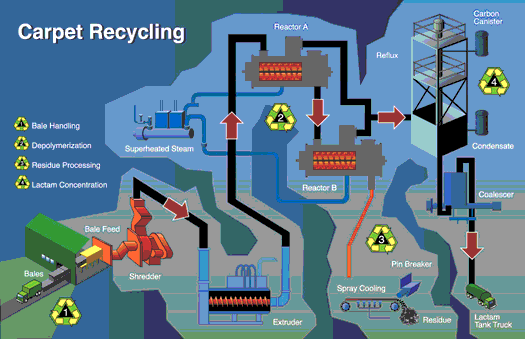
applications. Patented TechnologyNylon fibers can be recycled time and time again back to
their base material without any loss of properties. This post-consumer system is the most complete
form of recycling available, according to Lawson. The recycling process does not produce any waste.
Even the non-nylon 6 materials and the dirt present in used carpet (which, together, form 55
percent of carpet waste), are economically reused as a co-product.The ENR plant uses a jointly
developed, patented technology that depolymerizes nylon 6 into capro-lactam. Nylon 6 is used in
such applications as residential and com-mercial carpet, engineering plastics, automotive parts,
sporting goods, films and packaging. The facility will produce more than 100 million pounds of
caprolactam each year with the same performance and aesthetic qualities as virgin
caprolactam.Caprolactam is the primary raw material used in the production of nylon 6. At DCNAs
plant, it is stored in liquid form in tanks heated to a temperature of 170°F. Molten caprolactam is
shipped to domestic customers who convert it to nylon 6 for end-uses including carpet, tire cord,
monofilament (trimmer/edger line and fishing line) and engineered plastics. DCNA also cools the
molten capro-lactam into a solid state known as flake caprolactam. The flake is then packaged for
export sales primarily for textile applications (apparel and hosiery).The ENR facility is also a
model of energy efficiency, saving 700,000 barrels of oil and 4.4 trillion British Thermal Units
(BTUs) per year compared to conventional caprolactam production. Lawson noted this is enough energy
to heat 100,000 medium-sized homes for a year. Recycling AdvantagesThe key drivers for nylon
6-to-caprolactam recycling are as follows: Caprolactam can be produced economically with quality
equal to virgin material.Material life is extended, saving money in the business chain.The process
is environmentally sound from every aspect.Demand for materials and components with a recycled
content is growing.Because ENR can accept only nylon 6 waste, it became apparent from the start
there had to be a way to sort nylon 6 carpet from forms such as nylon 66 and polyester.Experienced
operators are critical to maintaining product quality. “Therefore, it is extremely important that
workers be trained properly in the use of sorting equipment and other markings, which can be used
to identify carpets,” Lawson said. Indentification CodesIdentification codes are printed
either directly on the back of the carpet as a string of letters or on an attached bar-code label.
This label is called a carpet component identification code (CCIC), which is a 7-digit alpha code
developed by the CarpetandRug Institute (CRI), Dalton, Ga., to identify the construction of a
carpet. This code has been used since 1996. Because the average life of a carpet is between eight
and 12 years, the only carpet likely to have the code on it today are remnants and installation
scraps.The most important digit in the code is the first letter. An A in this position indicates a
nylon 6 carpet, which is the type ENR recycles. B or C indicates a nylon 66 carpet. The second or
third code position identifies the type of primary and secondary backing used. An X in any position
indicates the manufacturer has not identified that part of the code. Melt Point
IndentificationThe simplest and least expensive type of sorting equipment currently identifies
carpet based on the melt point of its face fiber. A simple device can be made to identify carpet
based on the melt point. A device with two or three heated probes can be used to “brand” the
carpet.Such a device is commercially available from Cooper Tools under its brand name, Fiber-Rite.
The major drawback is its inability to distinguish between polyester and nylon 66. However, it
provides an inexpensive method that can be used to presort carpet. It can also be used to identify
carpets closer to their source, reducing the ultimate handling and disposal fees. Near
Infrared Sorting (NIR)The most accurate, reliable and versatile technique for identifying carpet is
based on near infrared (NIR) spectroscopy, according to Lawson. The carpet is illuminated using a
standard light source, and the reflected light is measured. Different materials absorb light
differently in various areas of the spectrum. By measuring and analyzing the reflected light, it is
possible to identify the face fiber type.CarPID, an NIR technology developed by DCNA and Honeywell,
is used as a portable instrument for the fast and safe identification of carpets according to their
face fiber type. The fiber materials nylon 6 (N6), nylon 66 (N66), polyester (PET), polypropylene
(PP) and wool (W) are distinguished. As with all commercially available NIR devices for sorting
carpet, a correct identification of blends is not guaranteed. Blends are normally classified and
displayed according to their major component. Sorting StandardsThere are known standards for
sorting that should be used to ensure that sorting equipment is functioning properly. “If there is
a question about the identity of the carpet, discard it,” Lawson said. Questionable carpets, he
suggested, could be blends. The dye-ability differences of face fibers are used to create styling
effects. For example, a three-color carpet with blue, gray and black, could contain nylon 6 as the
black fiber, nylon 66 as the gray fiber and polypropylene as the blue fiber.Operators can learn to
look for blends and pull the carpet when there is a question during testing. Lawson also said the
carpet should be tested on a clean, dry area. Impurities such as paint and moisture can cause
sorting errors.Another important area is cutting the carpet to be recycled. If using vertical
baling equipment, Lawson said it is best to cut the carpet to the width of the baler and make tight
rolls to place in the baler. “A best practice is to mark the width of the baler on the floor
directly in front of the baler,” he said. “Then the carpet can be spread out on the floor in front
of the baler and cut to the proper width with a rotary electric carpet cutter.”Lawson explained
there are two general types of balers used in the recycling industry: vertical down-stroke and
horizontal. The baler type is based on the orientation of the hydraulic ram used to compress the
material. A vertical baler has a vertical ram, and a horizontal baler has a horizontal
ram.Horizontal balers are generally larger and more expensive than vertical balers. Their advantage
is that they can usually produce larger, denser bales. Baling can also be automated to some extent
using equipment to tie the bale and compress it when the loading chamber is full.Vertical balers
are smaller, less automated and less expensive. They come in two classes: light-duty and
heavy-duty. Most pad recyclers use the light-duty balers for polyurethane foam. However, Lawson
recommended that, for post-consumer carpet, the recycler use a heavy-duty baler because it has a
heavier construction and a higher-horsepower hydraulic ram. Post-Industrial WasteIn addition
to carpet collection, post-industrial (P-I) nylon waste is also being collected throughout the
United States. Examples of P-I waste include waste from casting operations as well as yarn waste
from carpet manufacturers. P-I waste typically has a higher nylon 6 content than discarded carpet
and is valuable feedstock for ENR. As with carpet waste, ENR will divert a portion of P-I waste
from landfills and turn the waste into a product.ENRs system will allow Honeywell to produce its
Infinity, Forever Renewable Nylon, which is recycled and renewable in a truly closed-loop process.
All applications of nylon 6 are acceptable for Infinity nylon, including producing high-performance
carpet fibers with all the design and perform-ance characteristics of virgin nylon.DCNA will market
its share of the recycled caprolactam from the ENR facility under the trade name ReCap, which will
be available to the merchant caprolactam market. ReCap will also be marketed through DCNAs
downstream nylon polymer products, including carpet spinning chips and DSMs Akulon® Renew
engineering plastic resins.Lawson said ENR is working hard to ensure environmental excellence. “We
have made a strong commitment to this project, both emotionally and financially. Plus, we are
constantly searching for ways to make recycling easier and more affordable. We expect to continue
to be a leader in this industry.”
October 2000


 W
W